Induction Heat Staking a Wire Spring in a Wire Nut
Overview Heat staking is a critical process in many high‑volume manufacturing applications where metal components must be securely inserted into...
Processes
Processes: More
Processes: More

Industries:
Industries: More
Industries: More
Industries: More

Products:
Products: More
Services:
Services: More

Learn:
Learn: More
About:

1 min read
Brett Daly
3/28/17 3:22 PM
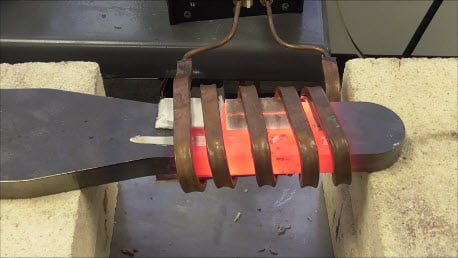
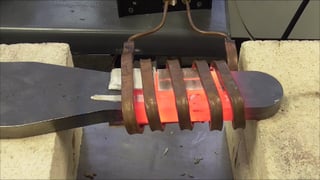
A client came to THE LAB looking to improve upon their heating process. They had been using a torch, but wanted a faster, safer, more repeatable method of heating. The objective of the application was to heat a magnetic steel part to 1700 ºF (927 ºC) for a forming application.
THE LAB determined that an Ambrell EKOHEAT 15 kW/50-150 kHz induction heating system would be optimal for this application. A specially designed single position multiple-turn helical coil was leveraged. Testing showed that heating to the targeted through-Curie temperature would take two minutes and twenty seconds.
The client benefitted from speed gains with this induction heating process along with greater safety and enhanced repeatability. And thanks to the expertise from THE LAB, the client knew exactly how induction would work with their application prior to making a system purchase.
Interested in learning about other forming/forging induction heating applications? Check out our application library and see how others have benefitted from the expertise of Ambrell's applications experts.

Overview Heat staking is a critical process in many high‑volume manufacturing applications where metal components must be securely inserted into...

Objective Removing rubber that has been permanently bonded to steel or other ferrous substrates can be a challenging and time consuming process....

In defense manufacturing, there is little margin for error. Components must meet exacting specifications, perform reliably in extreme environments,...